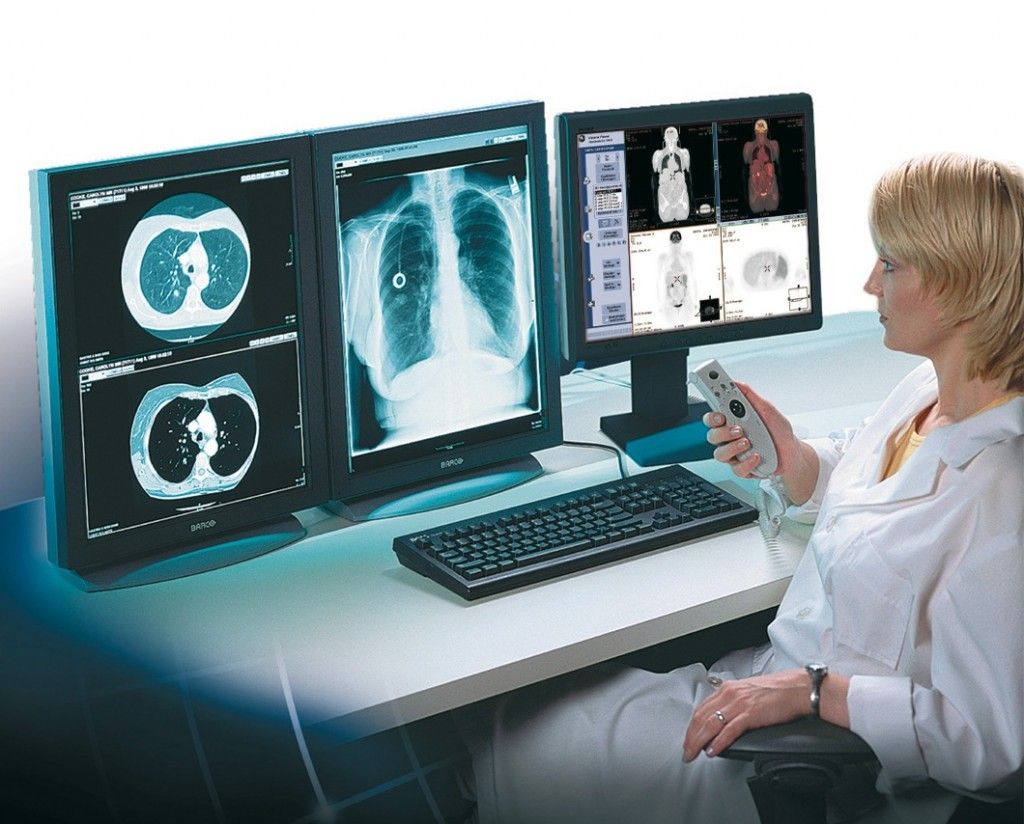
Radiology and imaging play a crucial role in modern healthcare systems. They provide invaluable insight into the internal structures and functions of the human body, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. With advancements in technology, radiology and imaging techniques have significantly evolved over the years, bringing about a revolution in the field of healthcare.
The Importance of Radiology and Imaging
Radiology and imaging techniques allow healthcare professionals to visualize and examine the internal organs, bones, tissues, and vessels without invasive procedures. This ability to generate detailed images helps in the early detection and accurate diagnosis of diseases and conditions, improving patient outcomes. Radiology and imaging are used across multiple medical specialties, including radiology, cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, gastroenterology, and neurology, to name a few. These techniques aid in the identification, characterization, staging, and monitoring of diseases, assisting the healthcare team in providing the most effective treatment plans.
Types of Radiology and Imaging Techniques
There are several different types of radiology and imaging techniques currently in use. Each technique has its own merits and is used in specific scenarios, based on the organs or systems being examined.
X-Ray Imaging
X-ray imaging is one of the oldest and most commonly used techniques. It involves passing X-rays through the body, which are absorbed differently by different tissues, creating an image that highlights abnormalities. X-rays are frequently used to identify fractures, tumors, infections, and other conditions affecting the bones and lungs.
Computed Tomography (CT)
CT scanning involves taking a series of X-ray images from different angles and using a computer to create a cross-sectional image. CT scans provide detailed views of various parts of the body, including the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. They are particularly useful in detecting tumors, injuries, and abnormalities in soft tissues.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of organs and tissues. MRI scans are especially useful for examining the brain, spinal cord, joints, and soft tissues, such as muscles and tendons. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for pregnant women and children.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the body's internal structures. It is commonly used in obstetrics and gynecology to monitor fetal development, as well as in assessing various organs, such as the liver, kidneys, heart, and blood vessels.
Nuclear Medicine Imaging
Nuclear medicine imaging involves the injection of radioactive substances into the body, which emit gamma rays. Special cameras detect these rays to create images that provide valuable information about organ function, such as the thyroid, heart, bones, and kidneys. This technique helps in diagnosing and monitoring conditions like cancer, heart disease, and thyroid disorders.
Advancements in Radiology and Imaging
Over the years, radiology and imaging have witnessed significant advancements, enhancing their effectiveness and accuracy. Technological innovations have driven the development of more powerful and efficient imaging machines, leading to improved image quality and reduced scan times. One such advancement is three-dimensional (3D) imaging, which provides a more detailed representation of the body's structures. With 3D imaging, healthcare professionals can obtain a better understanding of complex anatomical relationships and plan intricate surgical procedures with precision. Artificial intelligence (AI) has also made its way into radiology and imaging. AI algorithms have the potential to assist radiologists in interpreting scans, improving diagnostic accuracy, and reducing the chances of human error. Furthermore, AI-based tools can help identify patterns and predict disease outcomes, aiding in early intervention and personalized treatment plans.
The Future of Radiology and Imaging
The future of radiology and imaging is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts aiming to make further advancements. In the coming years, we can expect continued improvements in imaging resolution, speed, and portability. Emerging technologies, such as molecular imaging and functional imaging, hold great potential in providing more comprehensive information about disease processes at a cellular and molecular level. This can lead to early detection and targeted treatment approaches, significantly improving patient care and outcomes. Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is also making its way into the field of radiology and imaging. 3D printing allows for the creation of patient-specific models, aiding in surgical planning, medical education, and innovative research.
Conclusion
Radiology and imaging have become indispensable tools in modern medicine. The ability to visualize and analyze internal structures and functions has revolutionized the way diseases are diagnosed and treated. With ongoing advancements and the integration of cutting-edge technologies, radiology and imaging techniques are poised to continue transforming healthcare, leading to improved patient care and outcomes.